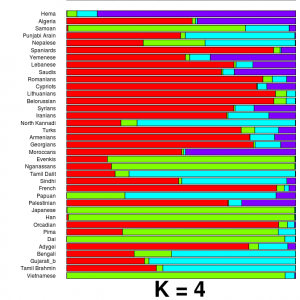
 Razib Khan, more known for his detailed low-downs of population biology and history, has written an important post on Gene Expression, explaining in careful detail exactly how to run some simple population genetic analysis on public genomes, as well as on your own personal genomics data. The outcome of the tutorial is an ADMIXTURE plot (like the one to the left), showing what proportion of your genome comes from different ancestral populations. This sort of analysis is not difficult, but it can often be hard to know how to start, so Razib’s post gives a good landing point for people who want to dig deaper into their own genomes.
Razib Khan, more known for his detailed low-downs of population biology and history, has written an important post on Gene Expression, explaining in careful detail exactly how to run some simple population genetic analysis on public genomes, as well as on your own personal genomics data. The outcome of the tutorial is an ADMIXTURE plot (like the one to the left), showing what proportion of your genome comes from different ancestral populations. This sort of analysis is not difficult, but it can often be hard to know how to start, so Razib’s post gives a good landing point for people who want to dig deaper into their own genomes.
This tutorial also ties in to some political ideas that Razib has been talking about since the recent call to allow access to genomic information only via prescription. If you are worried about losing access to your genome, one option is to ensure that you do not require companies to generate and interpret your genome. As sequencing, genotyping and computing prices fall, DIY genetics becomes more and more plausible. Learn to discover things about your own genome, and no-one will be able to take that away from you. [LJ]
 To celebrate 10 years since the back-to-back publications of complete human genomes in Science and Nature, Science has published series of articles looking back at the last 10 years of genomics, and forward to the future. The article contains short essays from Francis Collins and Craig Venter, the former talking about some of the successes of medical sequencing (including giving a name and photograph to the exome-sequenced IBD patient I
To celebrate 10 years since the back-to-back publications of complete human genomes in Science and Nature, Science has published series of articles looking back at the last 10 years of genomics, and forward to the future. The article contains short essays from Francis Collins and Craig Venter, the former talking about some of the successes of medical sequencing (including giving a name and photograph to the exome-sequenced IBD patient I  Of particular interest is an article by Eliot Marshall on why genomics hasn’t yet had a large effect on medical practice, and what needs to be done to allow the genomic revolution to trickle into medical care. He argues that scientists and doctors need to meet each other half way; scientists need to focus more on showing the direct clinical utility of genomics, whereas doctors need to be more ready to accept new technologies and discoveries, and adapt the way they practice medicine to make full use of them. [LJ]
Of particular interest is an article by Eliot Marshall on why genomics hasn’t yet had a large effect on medical practice, and what needs to be done to allow the genomic revolution to trickle into medical care. He argues that scientists and doctors need to meet each other half way; scientists need to focus more on showing the direct clinical utility of genomics, whereas doctors need to be more ready to accept new technologies and discoveries, and adapt the way they practice medicine to make full use of them. [LJ] Illumina CEO Jay Flatley announced that an upgrade to their HiSeq 2000 platform expected this spring will allow users to generate 600 gigabases of sequence (the equivalent of 5 high quality human genomes) per one-week run of the machine. This would essentially double the current throughput of the platform and propel Illumina even further ahead in the arms race of delivering vast quantities of low cost sequence data. [JCB]
Illumina CEO Jay Flatley announced that an upgrade to their HiSeq 2000 platform expected this spring will allow users to generate 600 gigabases of sequence (the equivalent of 5 high quality human genomes) per one-week run of the machine. This would essentially double the current throughput of the platform and propel Illumina even further ahead in the arms race of delivering vast quantities of low cost sequence data. [JCB] RSS
RSS Twitter
Twitter
Recent Comments